[rev_slider Slider6]
WHAT IS THE COGENERATION?
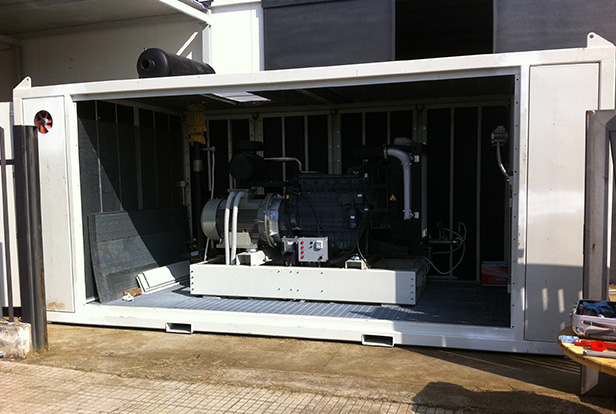
The word cogeneration stands for the combined production of electricity and heat, obtaining an overall performance from the conversion higher than the separated production method for electricity and heat.
The added value of a cogeneration system gives the possibility to produce electricity and at the same time to get back the heat that usually remains unused and dispersed in the atmosphere.
In other words, a cogeneration system can be seen as a generating sets which, instead of the only electricity production , get back also the heat generated, improving the overall performances.
THE TRIGENERATION
Ali6 develops also trigeneration plants from 20 to 200 Kw.
The trigeneration is the combined production of electricity, heat and refrigerating power.
The combined production can improve the efficiency of using fossil fuel over the 80%; and result in lower costs and lower level of pollutant emissions and greenhouse gas, compared to separate production of electricity and heat.
In the tertiary sector for temperate zones, the heat needed is restricted to few winter months, although there is a significant requirement for cold (air conditioning) during summer months. In this casem with a trigeneration plant, heat is used to produce cold through particular machines called “absorbers”.

 HOW IT WORK
HOW IT WORK
The generator used for the production of energy is typically an internal combustion engine and the operating principle is that of a generator, which burns fuel to produce electricity and heat simultaneously: normally the heat is dissipated through a radiator, in cogeneration instead, it is used to produce hot water usable for heating (T max 90 ° C).

ADVANTAGES

LOWER FUEL CONSUMPTION AND THEN MORE SAVINGS
Use of thermal energy otherwise not used, with a consequent saving of fuel.

LESS AIR POLLUTION
Reducing the environmental impact of the reduction of polluting emissions and less waste heat released into the environment.

DISTRIBUTED ENERGY PRODUCTION WITH SMALLER LOSS GLOBAL
Lower losses of transmission and distribution to the national electricity system arising from the location of the plants near the catchment areas and dall’autoconsumo energy produced.

TAX EXEMPTION FUEL
In the case of self-production of electricity, regional taxes and excise duties on fuel are defiscalizzate a function of electric power produced.

CONCESSIONAL RATES FOR WITHDRAWAL OF ELECTRICITY
Metering and dedicated withdrawal.

REVENUES FROM WHITE CERTIFICATES (TEE)
Incentives granted to primary energy savings achieved through interventions and projects to increase energy efficiency.

APPLICATIONS

RESIDENTIAL SECTOR
The residential sector, which is involved in the course of little cogeneration and which has a great unexpressed potential.

INDUSTRIAL SECTOR
The industrial sector, where the cogeneration plant are widespread especially inside big companies, but with still undiscovered markets as the wide range of small and medium size enterprises (SME)

TERTIARY SECTOR
The tertiary sector, which has registered in the last few years an improved rate of growth about the number of machines installed.

AGRICULTURAL SECTOR
In the agricultural sector the cogeneration could be applied for greenhouse heating, substratum heating and for micro-climatization as a defense for pests.



 DETAILS
DETAILS
 DETAILS
DETAILS
 DETAILS
DETAILS
 DETAILS
DETAILS